Before agriculture | what did people eat
For a long time, people believed that meat was a big part of what hunter-gatherers ate before farming became common. But because there aren’t many well-preserved human remains from ancient times, we don’t know much about what these early people actually ate. This period, called the Paleolithic era, was before humans started farming, which happened during the Neolithic transition.
During the Paleolithic era, people lived as hunter-gatherers. This means they hunted animals for meat and gathered plants, fruits, nuts, and seeds to eat. They relied on what nature provided rather than growing crops or raising animals like we do today. However, the exact balance of their diet remains uncertain because evidence from that time is scarce.
Archaeologists study ancient human remains and artifacts to learn about the past. While they have found tools and other artifacts that suggest hunting and gathering activities, finding well-preserved human remains is rare. When remains are discovered, they can provide valuable clues about the diet of ancient people through analysis of tooth wear patterns, isotopic analysis, and examination of gut contents.
A recent study
A recent study disagrees with the idea that ancient hunter-gatherers relied heavily on meat. It found evidence from Morocco showing that people 15,000 years ago preferred eating plants. This discovery is important because it’s the first time scientists have found strong proof of plant-based diets in a society that lived before farming became common.
The study used a method called isotopic analysis to examine the remains of these ancient people. It revealed that they consumed a lot of plants, which was surprising because earlier beliefs suggested they mostly ate meat. This new finding changes our understanding of how ancient humans lived and what they ate. It shows that plant foods were a significant part of their diet, challenging previous assumptions about the importance of meat in their meals. This research helps us learn more about the habits and lifestyles of early human societies before they started farming.
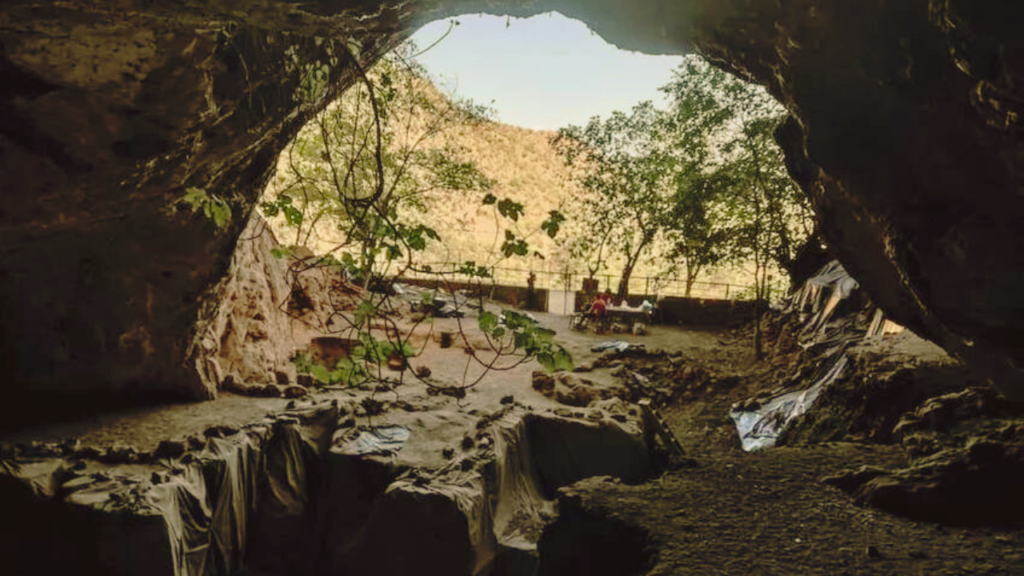
Live in cave
A group of scientists from different countries studied the diet of ancient people who lived in Morocco’s Taforalt cave. They used various methods to analyze the remains found there, like examining teeth and bones. Their research revealed that these ancient people ate a lot of plants, like acorns and pine nuts, even before farming started. This means they didn’t just rely on meat for food.
The study also found that plant-based foods were given to babies, suggesting they were part of their early diets. This is important because it shows that ancient communities might have started feeding babies plant foods earlier than we thought. Overall, the study helps us understand more about how ancient people lived and what they ate, challenging some of our previous ideas about their diets and habits.

Choose water over soda for summer hydration
Ancient societies had complicated diets before farming
This study challenges what we thought about what ancient people ate before farming. It also makes us curious why farming didn’t start in North Africa at the beginning of the Holocene period, a time when the Earth’s climate began to warm up.
Zineb Moubtahij, who led the study, says it’s really important to understand how people in different parts of the world survived long ago. By studying ancient diets, we can learn more about how humans evolved and spread to different places.
This research is the first to use a special method called zinc isotopes from teeth to learn about what ancient African people ate. North Africa is a key area for studying human history because it’s where many important events in our past happened. Having a new way to study what people ate there helps us understand how they lived and adapted to different environments.
In the future, the researchers want to explore more ancient sites in North Africa. They also want to try out new methods to learn even more about how ancient people ate. By doing this, they hope to uncover more secrets about our past and how we got to where we are today.